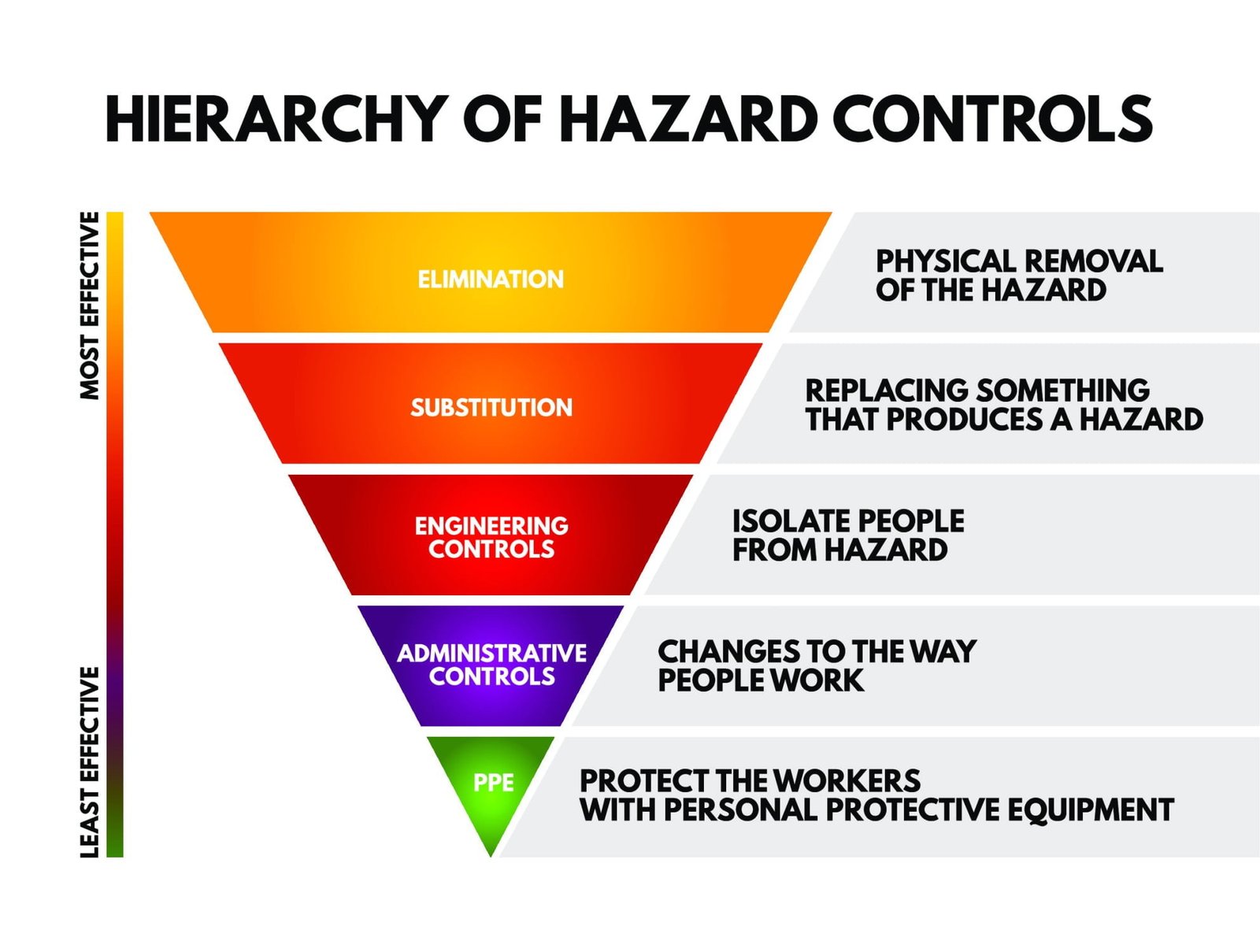
The Importance of a Safe System of Work for Confined Spaces
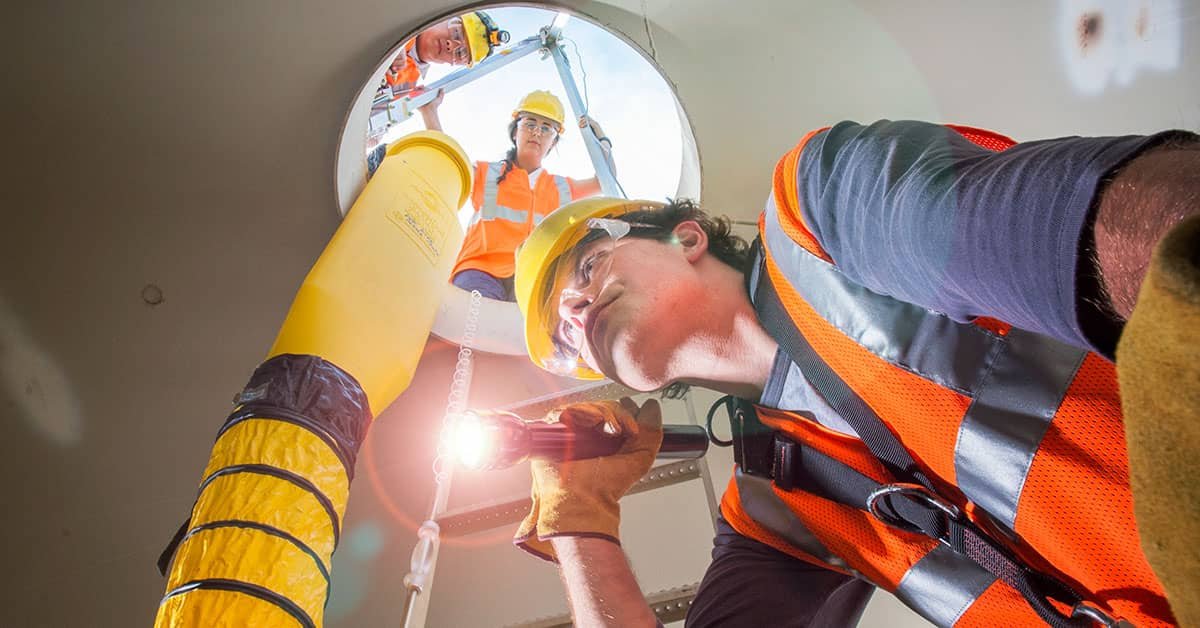
Confined spaces can present a range of hazards that can be potentially life-threatening. These spaces are characterized by limited entry and exit points, poor ventilation, and the potential for the accumulation of hazardous substances. In order to ensure the safety of workers who need to enter confined spaces, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive and effective safe system of work. This system should include several key elements to minimize risks and protect the well-being of those involved.
1. Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment is the foundation of any safe system of work for confined spaces. This involves identifying and evaluating the potential hazards present in the space, as well as assessing the likelihood and severity of any potential harm. The risk assessment should take into account factors such as the presence of toxic gases, lack of oxygen, extreme temperatures, and the potential for engulfment or entrapment. By understanding the risks involved, appropriate control measures can be implemented to mitigate these hazards.
2. Entry Permit System
An entry permit system is a vital component of a safe system of work for confined spaces. This system ensures that only authorized personnel who have received proper training and have the necessary equipment enter the confined space. The entry permit should outline specific precautions and procedures to be followed, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), communication methods, and emergency response protocols. The permit should be issued and signed off by a competent person who has conducted a thorough assessment of the conditions and risks.
3. Adequate Training and Supervision
Proper training is essential for all individuals involved in confined space work. This includes not only the workers who will be entering the space but also those who will be supervising the operation. Training should cover topics such as hazard identification, the correct use of equipment, emergency procedures, and the importance of communication. Supervisors should have a comprehensive understanding of the risks and control measures, as well as the ability to effectively monitor and manage the confined space operation. Ongoing training and refresher courses should also be provided to ensure that knowledge and skills are up to date.
4. Effective Communication
Clear and effective communication is crucial when working in confined spaces. This includes communication between workers inside the confined space and those outside, as well as communication between team members. Communication methods should be established before entering the confined space, and all workers should be aware of the procedures in place. This may include the use of radios, hand signals, or other suitable methods. Regular check-ins and a system for raising alarms or calling for help should also be established to ensure that any issues or emergencies can be quickly addressed.
5. Regular Monitoring and Review
A safe system of work for confined spaces should be regularly monitored and reviewed to ensure its effectiveness. This includes conducting regular inspections of the confined space, evaluating the control measures in place, and addressing any identified issues or deficiencies. Feedback from workers and supervisors should be encouraged and used to improve the system. It is important to keep up to date with changes in legislation, industry best practices, and technological advancements to continuously enhance the safety of confined space work.
Conclusion
Creating a safe system of work for confined spaces is essential to protect the well-being of workers and minimize the risks associated with these hazardous environments. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, implementing an entry permit system, providing adequate training and supervision, establishing effective communication methods, and regularly monitoring and reviewing the system, employers can ensure that their workers are able to carry out their tasks in a safe and controlled manner. Prioritizing safety in confined space work is not only a legal obligation but also a moral responsibility.