The meaning of hard hat colors has evolved significantly since the 1931 Hoover Dam project. A simple safety measure transformed into a vital identification system at construction sites.
Color-coded hard hats now act as visual markers that help everyone quickly spot different personnel roles and keep sites safe. This smart system came from World War II military practices that prevented confusion and made operations more efficient. OSHA regulations require hard hats to resist penetration, deflect blows, absorb shock, and provide electrical insulation.
This piece explains the eight standard hard hat colors, what they mean, and which roles they represent. Site managers, safety inspectors, and new workers need to know these color codes to keep construction sites safe and productive.
White Hard Hats: Leadership and Management Roles
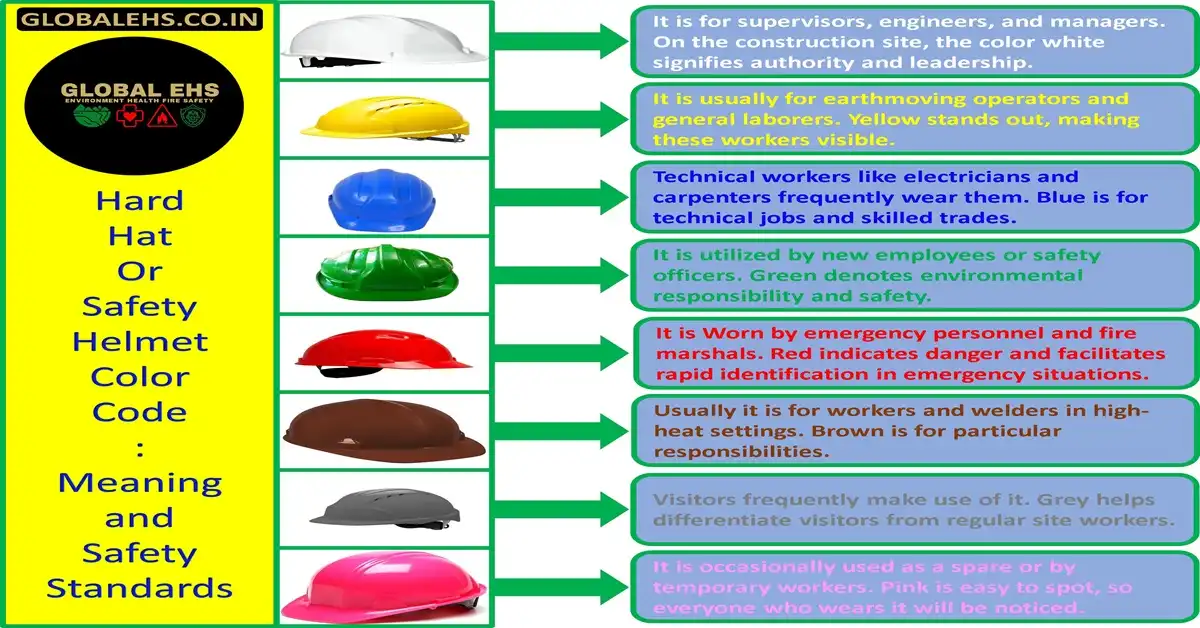
Image Source: Global EHS
White hard hats symbolize authority and leadership at construction sites. These distinctive helmets help workers spot personnel who oversee operations and keep everyone safe.
White Hard Hat Meaning and Significance
White hard hats mark executive and supervisory positions, which makes it easy to find someone when help or guidance is needed. The color shows higher rank at job sites and points to people with important decision-making roles.
Roles That Require White Hard Hats
These leadership positions need white hard hats:
- Site managers and supervisors
- Engineers and architects
- Project foremen
- Competent operatives
Safety Requirements for White Hard Hat Users
OSHA regulations state that all white hard hats must meet ANSI Z89.1 standards. These requirements include:
- Impact and penetration resistance testing
- Electrical insulation specifications
- Regular checks for damage or wear
The core team must also follow specific rules:
- No changes to the shell or suspension without manufacturer’s approval
- Daily checks for dents or cracks
- Proper fit without other headwear getting in the way
Identifying White Hard Hat Personnel on Site
You can spot white hard hat wearers by their other identifiers. Site managers typically wear formal clothes, while vehicle marshals must have Class 3 hi-visibility jackets. Some companies boost identification through:
- Names above company logos
- Organization titles below logos
- Reflective bands at the crown’s base
The white hard hat system creates clear communication paths at construction sites. Workers can quickly find supervisors to ask questions or raise safety concerns. This standard approach gives a professional look while keeping everything in safety protocols running smoothly across construction work.
In electrical work areas, white hard hat users need helmets that meet Class E specs to protect against high-voltage hazards up to 20,000 volts. Hard hat zones must have clear signs that show head protection requirements at every entry point.
Yellow Hard Hats: General Construction Workers

Image Source: Global EHS
Yellow hard hats are everywhere on construction sites. They’re the most common safety gear worn by general workers and earth-moving operators. These workers are the core team members who keep construction projects running smoothly.
Understanding Yellow Hard Hat Applications
Yellow hard hats help identify general laborers and equipment operators quickly. These workers need complete focus when they work, especially with heavy machinery. The bright yellow color makes them easy to spot in busy construction areas, which helps everyone work safely and efficiently.
Key Responsibilities of Yellow Hard Hat Wearers
Workers who wear yellow hard hats handle several vital tasks:
- Operating heavy machinery and equipment
- Executing earth-moving operations
- Conducting trench digging activities
- Managing loading and unloading operations
Safety Protocols for General Construction Workers
Construction ranks among the most dangerous industries, with many workplace injuries and deaths. Yellow hard hat wearers must follow complete safety measures strictly:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Requirements:
- Regular inspection of hard hats for wear and tear
- Proper fit without modifications
- Use of additional safety gear like earplugs and safety glasses
Workers wearing yellow hard hats must stay alert to spot potential risks. They need to watch out for:
- Slip-and-fall dangers
- Equipment malfunctions
- Tool-related accidents
- Heat stress risks during outdoor work
Construction sites need strict safety rules, particularly for heavy machinery work. Only trained workers should operate equipment. Specialized machinery like forklifts and cranes require extensive safety training.
Yellow hard hat workers also attend regular safety meetings to learn about new safety practices. These sessions help them understand proper procedures and address specific risks in their daily work. Good training and constant awareness help these workers stay safe while they do their essential work.
Blue Hard Hats: Technical Specialists

Image Source: Architecture Lab
Technical specialists at construction sites wear blue hard hats that set them apart from other workers. These professionals excel at specialized tasks because of their expertise and training.
Blue Hard Hat Role Classification
Blue hard hats identify skilled technical workers who include:
- Electricians who work on wiring and electrical systems
- Carpenters who handle construction woodwork
- Plumbers who work on water systems
- Technical advisors who oversee specialized operations
Sometimes, temporary employees and technical consultants also wear blue hard hats. This shows their specialized roles but limited knowledge of site hazards.
Technical Worker Safety Requirements
Blue hard hat workers must follow strict safety protocols due to their specialized work:
- They must check their equipment before starting technical tasks
- They need to follow electrical safety standards strictly
- They should use specialized tools safely
- They must work together with other technical teams on site
Safety management software tracks these requirements. This makes quick responses to risks possible and improves overall safety strategies. Technical specialists need regular training to keep up with new construction techniques and materials.
Identifying Blue Hard Hat Personnel
Blue hard hat workers stand out clearly among general laborers who wear yellow hats. This visual difference serves several purposes:
- People can quickly find technical experts during emergencies
- The quickest way to assign specialized work becomes clear
- Technical operations get proper supervision
- The right people handle specific technical jobs
Technical specialists must work closely with general contractors and construction managers at sites with multiple employers. This collaborative effort will give a proper protection for everyone involved in technical operations.
Blue hard hat workers take part in regular safety meetings and toolbox talks. These sessions help them stay aware of site hazards and remember proper safety steps. Clear identification and following safety rules help blue hard hat personnel stay safe while they do their specialized work. Their actions keep the entire site secure too.
Orange Hard Hats: Traffic and Crane Operations
Orange hard hats play a vital role in traffic control and crane operations at construction sites. Worker safety depends on high visibility in these environments. The numbers tell a concerning story – 64% of highway contractors faced crashes at their worksites in 2022.
Orange Hard Hat Usage Guidelines
Workers wearing orange hard hats take on specialized duties that include:
- Road construction operations
- Traffic control and marshaling
- Crane operations and signaling
- Heavy equipment movement coordination
These workers need specific qualifications to sling weights and give precise hand signals to crane operators. Their knowledge will give a safe weight distribution and lifting operations throughout construction zones.
High-Visibility Requirements
ANSI/ISEA Z89.1-2014 sets strict standards for high-visibility hard hats:
- Must meet specific chromaticity range requirements
- This is a big deal as it means that luminance specifications
- Requires ‘HV’ marking for ANSI compliance
- Must be visible from a minimum distance of 1,000 feet
Safety Protocols for Traffic Control
The Federal Highway Administration requires specific rules for traffic control workers:
- Workers exposed to public traffic must wear high-visibility apparel
- State-specific regulations must be followed strictly
- Traffic control techniques require regular safety training
- Work zones need proper setup procedures
Crane Operation Standards
OSHA guidelines outline detailed safety measures for crane operations:
- Personnel platforms must maintain clear operator visibility
- Personnel hoisting requires slow, controlled movements
- Protection from potential overhead hazards
- Safety equipment needs regular inspection
The Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) states workers near public access roadways must wear high-visibility safety apparel. States like New York and Missouri require both high-visibility hard hats and additional protective gear for road crews.
Orange hard hat wearers maintain vital safety standards in high-risk areas through proper training and safety protocols. Their distinctive color coding helps prevent accidents in chaotic environments, especially during low-visibility conditions or nighttime operations.
Green Hard Hats: Safety Personnel

Image Source: Architecture Lab
Green hard hats serve two important roles in construction site safety. They help identify experienced safety inspectors and new workers who need extra attention. The color makes it easy to spot safety personnel quickly in busy construction areas.
Green Hard Hat Identification
Safety inspectors who wear green hard hats are the main guardians of workplace safety. These professionals check equipment, monitor safety rules, and make sure protective measures work properly. New workers also wear green hard hats to show they’re still learning, which signals others to be more careful around them.
Safety Inspector Responsibilities
Safety officers with green hard hats watch over construction operations by:
- Checking sites and equipment to spot potential risks
- Creating and putting safety protocols in place
- Recording safety issues and incident reports
- Managing emergency response procedures
These professionals work closely with company executives to meet safety goals. Their presence makes workers feel comfortable reporting hazards without worrying about the consequences.
New Worker Training Protocols
New staff wearing green hard hats must complete specific training:
- Learning about the site and its layout
- Understanding how to use safety equipment
- Learning to spot construction hazards
- Training for emergency response
Safety officers make sure protective gear stays in good condition through strict rules:
- Looking for damage on hard hat shells
- Testing suspension systems and chin straps
- Making sure everything fits right
- Keeping inspection records
Safety standards remain high thanks to green hard hat wearers who run daily checks, lead safety meetings, and update rules based on new risks. They do more than just follow rules – they help create a workplace where safety becomes second nature.
Red Hard Hats: Emergency Response

Image Source: Hard Head Veterans
Fire marshals and emergency responders who wear red hard hats protect workplaces from accidents and disasters. These professionals stay ready to act quickly by following detailed safety protocols and doing regular drills.
Red Hard Hat Emergency Protocols
Red hard hat personnel must follow strict emergency response guidelines:
- Sound alarms as soon as they spot hazards
- Guide evacuations through marked routes
- Check every floor to make sure everyone is out
- Take roll calls at assembly points
Fire Marshal Duties
Fire marshals handle key safety tasks:
- Make sure fire codes and building rules are followed
- Check fire permit requests
- Look into risks and investigate fires
- Write up safety violations
Emergency Response Coordination
Emergency response teams stay prepared by:
- Checking emergency equipment regularly
- Keeping fire logbooks and safety records up to date
- Working with local fire departments
- Setting up emergency communication systems
Safety Training Requirements
Red hard hat personnel learn about:
- Ways to prevent fires
- Steps to take in emergencies
- How to give first aid
- Safe handling of dangerous materials
Red hard hat personnel’s emergency response kit has important safety gear like flashlights, first aid supplies, and protective equipment. These professionals keep watch to make sure combustible materials are stored safely and no-smoking rules are followed.
Fire marshals check construction sites for dangers and inspect emergency exits, fire doors, and safety equipment often. They work with property managers and business owners to meet National Fire Protection Association standards, especially the Life Safety Code.
When emergencies happen, red hard hat wearers guide people to safety. They pay special attention to those who need extra help, like people who have trouble moving or seeing. Their bright red hard hats make them easy to spot in busy construction areas, so they can respond right away.
Brown Hard Hats: High-Heat Operations

Image Source: LinkedIn
Brown hard hats are vital for professionals who work in high-temperature environments. These protective helmets help keep welders and workers safe when they face intense heat conditions. Advanced materials and strict safety standards make these helmets highly effective protection gear.
Heat Protection Standards
Safety tests for brown hard hats ensure they provide the best protection in high-heat conditions. These helmets stay strong even at temperatures up to 350°F. ANSI/ASSP A10.50-2024 requires a complete heat stress management plan that covers:
- New employees need 5-7 days to get used to the conditions
- Workers must take scheduled breaks in shaded areas
- Everyone should drink plenty of water and electrolytes
- A buddy system helps monitor worker safety
Welding Safety Requirements
Welders face special risks that need extra protection. Brown hard hats come with features specifically made for welding work:
- They stop sparks and hot debris
- The helmet blocks welding torch glare
- Face shields and eye protection fit perfectly
- Materials resist heat during long work hours
Material Specifications
Brown hard hats are built tough and heat-resistant with:
- Shells made from fiberglass or carbon fiber
- ANSI Type I rated protection for the head
- Different suspension systems including ratchet, swingstrap, or pinlock
- Suspension parts must be replaced every 12 months
Workers must check these helmets regularly for heat damage and wear. Recent data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics shows 436 workers died from heat exposure between 2011 and 2021. This number shows why proper heat protection equipment matters so much.
Leading companies like MSA, Bullard, and Honeywell make brown hard hats that meet strict safety rules. The helmets’ adjustable systems ensure they fit well and stay comfortable during long shifts in hot conditions. Regular maintenance and timely replacements help workers stay protected from heat hazards in tough industrial settings.
Gray Hard Hats: Visitors and Temporary Workers

Image Source: Hard Head Veterans
Construction sites use gray hard hats to identify visitors and temporary workers who need extra guidance. This simple color system helps regular workers spot and assist people who might not know their way around hazards.
Visitor Safety Guidelines
Site managers follow detailed safety rules for visitors. Everyone must wear proper protective gear. Along with gray hard hats, visitors need:
- Safety glasses that meet ANSI Z87.1 standards
- High-visibility vests to stay visible
- Sturdy footwear with heavy-duty soles
Temporary Access Protocols
Visitors must complete these steps before entering the site:
- Submit visit requests 24 hours early
- Get their badge at visitor control
- Have their PPE checked and fitted
- Take a quick safety briefing
Regular workers help anyone wearing gray hard hats stay away from dangerous spots and warn them about possible hazards. Bright pink helmets serve as backups when visitors misplace their gray ones.
Site Orientation Requirements
The site’s orientation process covers three main areas:
Basic safety rules come first, including how to use PPE and handle emergencies. Next, visitors learn site-specific details like speed limits, off-limits areas, and chemical hazards.
The emergency training teaches visitors about:
- What different alarms mean
- Where to go during evacuations
- How to report incidents
- Ways to identify response teams
Site managers keep logs of each visitor’s details, time on site, and visit purpose. Authorized guides must stay with visitors at all times to prevent them from wandering into work areas.
OSHA rules make host employers responsible for temporary worker safety, including choosing and providing PPE. These safety protocols help construction sites protect visitors while meeting regulations and keeping operations running smoothly.
Comparison Table
| Hard Hat Color | Primary Users/Roles | Key Responsibilities | Safety Requirements | Special Features/Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | Site managers, engineers, architects, project foremen | Oversee operations, keep workers safe, make critical decisions | Must meet ANSI Z89.1 standards, needs daily visual checks | Name goes above company logo, formal attire, Class 3 hi-visibility jackets for vehicle marshals |
| Yellow | General construction workers, earth-moving operators | Operate heavy machinery, dig trenches, handle loading/unloading tasks | Check PPE regularly, ensure proper fit, use extra safety gear (earplugs, safety glasses) | Most common on construction sites, workers need constant watchfulness against hazards |
| Blue | Electricians, carpenters, plumbers, technical advisors | Handle specialized technical work, maintain systems, provide technical guidance | Check equipment regularly, follow electrical safety standards | Different from general workers, needs special tool safety measures |
| Orange | Traffic controllers, crane operators | Direct traffic, run cranes, coordinate heavy equipment movement | Meets high-visibility rules per ANSI/ISEA Z89.1-2014, visible from 1,000 feet | HV marking meets ANSI rules, wear with extra high-visibility gear |
| Green | Safety inspectors, probationary workers | Check sites, implement safety rules, spot hazards | Check protective gear regularly, document safety issues | Serves two purposes: shows both safety staff and new workers |
| Red | Fire marshals, emergency responders | Coordinate emergency response, manage evacuations, oversee fire safety | Complete fire prevention training, first aid, hazmat handling | Carry emergency response kit, need quick identification |
| Brown | Welders, high-heat operation workers | Handle high-temperature work, perform welding | Heat resistant up to 350°F, check often for heat damage | Uses special materials (fiberglass/carbon fiber), works with face shields |
| Gray | Visitors, temporary workers | Access limited areas, follow guided tasks | Complete safety training, wear full PPE | Need authorized escort, visitor badges, must check in |
Conclusion
Hard hat color coding is a crucial safety system at construction sites that has grown since the 1931 Hoover Dam project into today’s complete identification system. The color scheme serves specific purposes. White hats identify leadership roles, while yellow ones mark general workers. Technical specialists wear blue, and traffic controllers use orange. Safety personnel don green hats, emergency responders wear red, high-heat operators use brown, and visitors get gray ones.
These color codes may look simple but they follow strict safety standards that protect workers. Each role has unique safety requirements. White-hatted managers need electrical insulation protection, and brown-hatted welders must have heat-resistant gear.
Hard hat colors create safer construction sites by helping workers quickly identify personnel and their roles. Everyone on site needs this knowledge, from seasoned supervisors to new visitors. The protective measures work best with consistent training, proper hat maintenance, and strict safety protocols.
Construction projects succeed when teams properly follow safety standards, starting with the right hard hat usage. These color codes act as silent signals that keep order and safety in busy construction areas and protect workers every day.
FAQs
While there are common color associations, hard hat colors are not universally standardized. Different sites may have their own color-coding systems. Generally, white is often used for managers/supervisors, yellow for general workers, blue for technical specialists, and green for safety personnel.
According to OSHA regulations, employers are responsible for providing hard hats and other necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) to workers. Employees should not have to purchase their own hard hats for work purposes.
Construction hard hats must meet ANSI Z89.1 standards, which include specifications for impact resistance, penetration resistance, and electrical insulation. Hard hats should be regularly inspected for damage and replaced as needed.
While workers can purchase their own hard hats, it’s generally recommended to use employer-provided PPE. Using non-approved hard hats may create liability issues if an injury occurs. Always check with your employer before using personal protective equipment.
Hard hats should be replaced immediately if they sustain an impact or show signs of damage. Even without visible damage, manufacturers typically recommend replacing the suspension every 12 months and the entire hard hat every 5 years due to degradation from environmental exposure.

![8 Hard Hat Colors Meaning: Safety Guide for Construction Sites [2025]](https://hsestudy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Myshell_ThumbMaker_250224_190617-860x484.png)
![Fire Triangle vs Fire Tetrahedron: Which Model Better Explains Combustion? [2025]](https://hsestudy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Myshell_ThumbMaker_250224_185218-150x150.png)
